 Exchanging Messages
Exchanging Messages 
 Exchanging Messages Exchanging Messages | Table of Content | Configuring the Engine |
| Message Sequence Numbers |
A single FIX session can exist across multiple sequential (not concurrent) physical connections. Parties can connect and disconnect multiple times while maintaining a single FIX session. That is, once the Logout() method is called, the FIX Connection is terminated. However, when the FIX Connection is terminated, the FIX session doesn't end its lifetime. It is possible to continue the session later using either LogonAsAcceptor() or LogonAsInitiator(String, Int32) methods again. In other words, FIX Session is comprised of one or more FIX connections.
All FIX messages are identified by a unique sequence number (the MsgSeqNum field) within the bounds of a single FIX session. Sequence numbers are initialized at the start of each FIX session starting at 1 (one) and increment throughout the session. Each session establishes an independent incoming and outgoing sequence series.
OnixS .NET Framework FIX Engine automatically synchronizes sequence numbers when reconnecting during a FIX session on the basis of the information that was previously stored in the Engine log files.
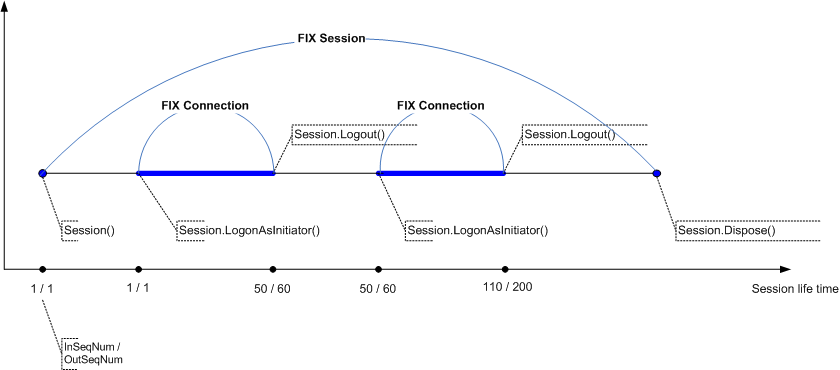
The sequence numbers monitoring enables parties to synchronize applications gracefully when reconnecting during a FIX session. To get the expected sequence number of the next incoming message, the InSeqNum property is exposed, as well as the OutSeqNum property, to get the sequence number of the next outgoing message.
Resetting inbound and outbound message sequence numbers back to 1, for whatever reason, constitutes the beginning of a new FIX session. Method ResetLocalSequenceNumbers() must be used to back up the previous log files and reset the sequence numbers to 1.
| Both InSeqNum and OutSeqNum properties can be used to set expected sequence numbers manually before a FIX connection is established. However, it is NOT recommended to use these properties to reset the message sequence numbers to 1 for the session. Instead, method ResetLocalSequenceNumbers() must be used. |
Some implementations of the FIX protocol expect that a FIX Session coincides with a FIX Connection. In other words, message sequence numbers must be reset back to 1 after the Logout messages exchange and the FIX connection is terminated.
To interact with such FIX venues, keepSequenceNumbersBetweenFixConnections parameter of Session(String, String, ProtocolVersion, Boolean) constructor should be set to false. In this case after the Logout() method sequence numbers are set back to 1. Next time when the Session object is created incoming and outgoing message sequence numbers will start from 1 (in other words, a new FIX Session will be created).